Molecular biomarkers involved in the progression of gallbladder inflammatory lesions to invasive cancer: A proteomic approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10704Keywords:
Liquid chromatography-assisted tandem mass spectrometry, biomarker, differentially expressed proteins, gallbladder cancer, ELISA, real time-polymerase chain reaction, inflammatory lesionAbstract
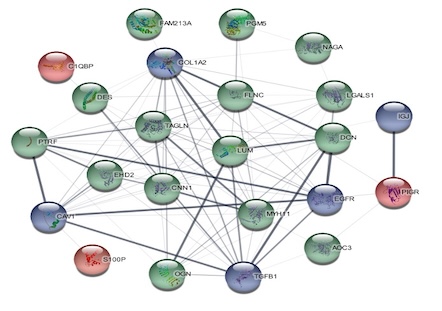
The progression of gallbladder inflammatory lesions to invasive cancer remains poorly understood, necessitating research on biomarkers involved in this transition. This study aims to identify and validate proteins associated with this progression, offering insights into potential diagnostic biomarkers for gallbladder cancer (GBC). Label-free liquid chromatography-assisted tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) proteomics was performed on samples from ten cases each of GBC and inflammatory lesions, with technical duplicates. Validation was conducted through the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using 80 samples (40 GBC and 40 inflammatory lesions). Bioinformatics tools analyzed protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks and pathways. Statistical correlations with clinicopathological variables were assessed. Prognostic evaluation utilized Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and Cox regression analyses. mRNA expressions were studied using real-time-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Out of 5714 proteins analyzed, 621 were differentially expressed. Three upregulated (the S100 calcium-binding protein P [S100P], polymeric immunoglobulin receptor [PIGR], and complement C1q-binding protein [C1QBP]) and two downregulated (transgelin [TAGLN] and calponin 1 [CNN1]) proteins showed significant expression. Pathway analysis implicated involvement of proteoglycans in cancer and glycosaminoglycan metabolism. Significant correlations were observed between protein concentrations and clinicopathological variables. Prognostic factors, such as tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and preoperative bilirubin levels were associated with overall survival (OS). Protein-based assays demonstrated higher resolution compared to mRNA analysis, suggesting their utility in GBC risk stratification. S100P, PIGR, C1QBP, TAGLN, and CNN1 emerge as potential protein-based biomarkers involved in the progression from gallbladder inflammatory lesions to invasive cancer. These findings hold promise for improved diagnostic and prognostic strategies in GBC management.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neetu Rawal, Gururao Hariprasad, Sabyasachi Bandyopadhyay, Nihar Ranjan Dash, Sunil Kumar, Prasenjit Das, Sharmistha Dey, Maroof Ahmad Khan, Amar Ranjan, Anita Chopra, Sundeep Saluja, Showket Hussain, G.K. Rath, Tanvir Kaur , Pranay Tanwar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









