Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index as a novel comprehensive biomarker in predicting the radiation-induced trismus rates in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10616Keywords:
Radiation-induced trismus, Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI), concurrent chemoradiotherapy, nasopharyngeal carcinomaAbstract
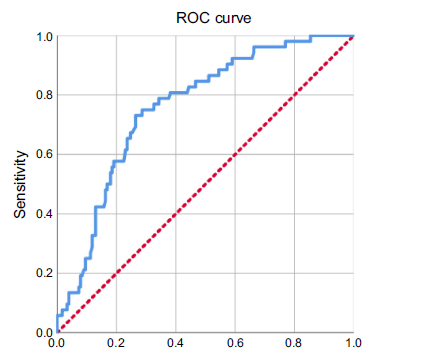
In this study, we aimed to evaluate whether the novel pretreatment Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) can predict radiation-induced trismus (RIT) in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (LA-NPC) patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT). Data of LA-NPC patients presenting without RIT were reviewed retrospectively. Any post-CCRT maximum mouth openings (MMO) ≤ 35 mm were considered RIT. The GINI index was calculated using the formula: GINI = (CRP x Monocytes x Platelets x Neutrophils) ÷ (Albumin x Lymphocytes). We used receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis to examine the potential correlation between pretreatment GINI measures and post-CCRT RIT status. Logistic regression analysis examined the independence of the association between confounding factors and RIT rates. The study comprised 230 participants, and 52 (22.6%) received an RIT diagnosis. The optimal pre-CCRT GINI cutoff that dichotomizes RIT rates was determined to be 1,424 (area under the curve [AUC]: 76%; sensitivity: 75.0%; specificity: 71.7%; J-index: 0.463). RIT incidence was significantly higher in the GINI ≥ 1424 group than in its GINI < 1424 counterpart (43.3% vs. 9.3%; hazard ratio: 4.76; P < 0.001). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that a pre-CCRT GINI ≥ 1424 was an independent predictor of increased RIT rates after definitive CCRT in this patient group (P < 0.001). In conclusion, the present results revealed that elevated pre-CCRT GINI measures (≥ 1424) can efficiently and independently predict elevated RIT rates in LA-NPC patients after CCRT.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study's findings is available from the corresponding author, Efsun Somay, upon a reasonable special request.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Efsun Somay, Erkan Topkan, Sibel Bascil, Nilüfer Kılıc Durankuş , Şükran Seyürek, Düriye Ozturk, Berrin Pehlivan, Ugur Selek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









