Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro–in ovo toxicological screening of silibinin fatty acids conjugates as prodrugs with potential biomedical applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10600Keywords:
Silibinin (SIL), oleic acid (OA), linoleic acid (LA), derivatization, physicochemical characterization, cytotoxicity, cell migration, irritant effectAbstract
This article has been corrected. Correction: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/12570
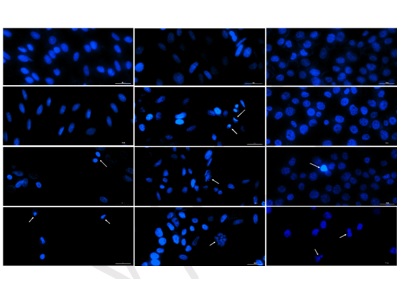
Silibinin (SIL), the most active phytocompound from Silybum marianum (L.), exerts many biological effects but has low stability and bioavailability. To overcome these drawbacks, the current research proposed the synthesis of silibilin oleate (SIL-O) and silibilin linoleate (SIL-L) derivatives as prodrugs with potentially optimized properties for biomedical applications, and the establishment of their in vitro–in ovo safety profiles. The physicochemical characterization of the obtained compounds using density functional theory (DFT) calculations, and Raman and 1H liquid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy confirmed the formation of SIL-O and SIL-L complexes. Computational predictions revealed that these lipophilic derivatives present a lower drug-likeness score (−29.96 for SIL-O and−23.55 for SIL-L) compared to SIL, but an overall positive drug score (0.07) and no risk for severe adverse effects. SIL-O and SIL-L showed no cytotoxicity or impairment in cell migration at low concentrations, but at the highest concentration (100 μM), they displayed distinct toxicological profiles. SIL-L was more cytotoxic (on cardiomyoblasts – H9c2(2-1), hepatocytes – HepaRG, and keratinocytes – HaCaT) than SIL-O or SIL, significantly inhibiting cell viability (<60%), altering cellular morphology, reducing cell confluence (<70%), and inducing prominent apoptotic-like nuclear features. At the concentration of 100 μM, SIL-O presented an irritation score (IS) of 0.61, indicating a lack of irritant effect on the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM), while SIL-L was classified as a slight irritant with an IS of 1.99. These findings outline a more favorable in vitro and in ovo biocompatibility for SIL-O compared to SIL L, whose applications are dosage limited due to potential toxicity.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Iasmina Marcovici, Simona Cinta Pinzaru, Adrian Pirnau, Vasile Chis, Andrea Simion, Geza Lazar, Andrada Iftode, Ersilia Alexa, Cristina Dehelean, Estera Boeriu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









