Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in neoadjuvant and concurrent chemoradiotherapy for refractory cervical cancer patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10528Keywords:
Refractory cervical cancer (CC), bevacizumab, neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT)Abstract
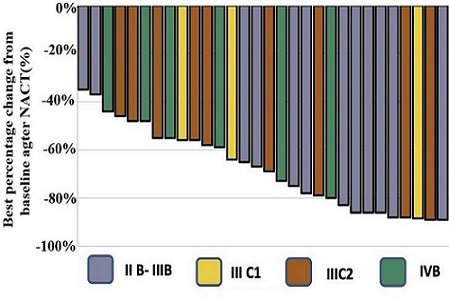
A platinum-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) is the standard treatment for refractory cervical cancer (CC). However, the recurrence of disease and the occurrence of metastasis remain prevalent. We observed the long-term efficacy and safety of bevacizumab combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) and CCRT in refractory CC. A total of 62 patients with refractory CC were enrolled in this study from January 2016 to December 2019. The NACT regimen included bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg), docetaxel (75 mg/m2), and cisplatin (75 mg/m2), administered tri-weekly for 2 cycles. The CCRT regimen included bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2), administered tri-weekly for 2 cycles. A dose of 45-50 Gy was prescribed for external beam radiotherapy (EBRT), while 30-35 Gy in 4-5 fractions was prescribed for brachytherapy (BT). Among the patients, 21 patients (33.9%) were at stages IIB-IIIB, 8 patients (12.9%) were at stage IIIC1, 19 patients (30.6%) were at stage IIIC2, and 14 patients (22.6%) were at stage IVB. Pelvic, para-aortic, supraclavicular, and inguinal lymph node metastases were discovered in 41 patients (66.1%). The median follow-up was 49.8 months (12.3-82.7 months). The median tumor volumes pre-treatment, after NACT, and before BT were 84.64 ± 53.15 cm3, 1.64 ± 13.15 cm3, and 0 ± 1.5 cm3, respectively. Complete clinical response (cCR) rates after NACT and EBRT were 35.5% and 66.1%, respectively. Four years after the diagnosis, the overall survival (OS) rate was 78.6%, the local region-free survival (LRFS) rate was 91.3%, the disease-free survival (DFS) rate was 70.6%, and the distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) rate was 81.4%. A total of 29 patients (46.8%) experienced grade 3/4 hematological toxicity, 3 patients (4.8%) experienced grade 3 gastrointestinal toxicities, and none experienced grade 5 adverse events. Bevacizumab combined with NACT and CCRT significantly improved cCR and OS in refractory CC with acceptable toxicity.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hua Yang, Shi Gao Huang, Mohan Dong, Xiaomeng Wang, JunHua He, Huyan Su, Changhao Liu, Yong Zhu, Lichun Wei, Zi Liu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









