Association between serum galectin-3 and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10527Keywords:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, galectin-3, acute exacerbation, biomarkerAbstract
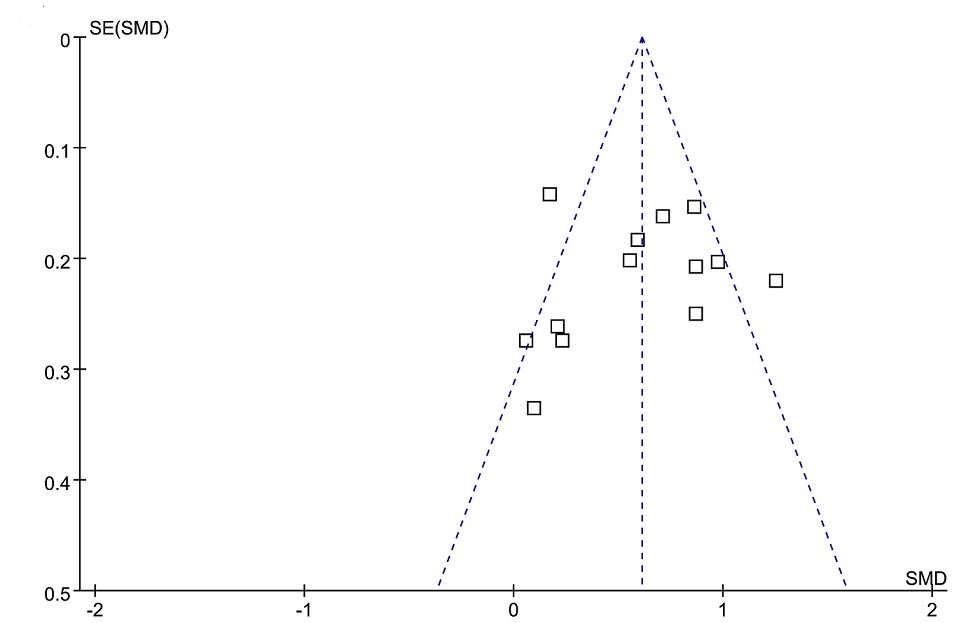
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a significant public health issue characterized by progressive and irreversible airflow limitation. The aim of this meta-analysis was to determine the association between changes in serum galectin-3 levels and COPD and to assess the relationship between serum galectin-3 levels and acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD). Relevant observational studies were retrieved from electronic databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Wanfang, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). A random-effects model was used to combine the data, incorporating the influence of between-study heterogeneity. Twelve case-control studies were included. The pooled results showed a significantly higher serum level of galectin-3 in patients with COPD compared to controls (standardized mean difference [SMD] 0.60; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.40 - 0.80; P < 0.001; I2 = 68%). Further meta-analysis suggested higher levels of serum galectin-3 in patients with AECOPD compared to those with stable COPD (SMD 0.33; 95% CI 0.20 - 0.46; P < 0.001; I2 = 0%). Subgroup analyses according to the mean age of the participants, the proportion of males, and study quality scores did not significantly change the results (P for subgroup differences all > 0.05). In conclusion, patients with COPD were found to have higher serum levels of galectin-3, with levels further elevated in patients with AECOPD compared to those with stable COPD.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
All the data generated during the study are included within the manuscript.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Xiangyu Zhao, Bo Han, Wentao Tang, Shanshan Ji, Lie Wang, Jinbao Huang, Yizhong Hu, Jie Li

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









