CTHRC1 is associated with BRAF(V600E) mutation and correlates with prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and drug resistance in colon cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10397Keywords:
CTHRC1, BRAF(V600E), colon cancer, thyroid cancer, melanomaAbstract
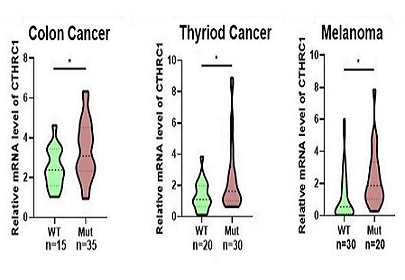
Colon cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma are common malignant tumors that seriously threaten human health globally. The B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF)(V600E) mutation is an important driver gene mutation in these cancer types. In this study, we identified that collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 (CTHRC1) expression was associated with the BRAF(V600E) mutation in colon cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma. Based on database analysis and clinical tissue studies, CTHRC1 was verified to correlate with poor prognosis and worse clinicopathological features in colon cancer and thyroid cancer patients, but not in patients with melanoma. Several signaling pathways, immune cell infiltration, and immunotherapy markers were associated with CTHRC1 expression. Additionally, a high level of CTHRC1 was correlated with decreased sensitivity to antitumor drugs (vemurafenib, PLX-4720, dabrafenib, and SB-590885) targeting the BRAF(V600E) mutation. This study provides evidence of a significant correlation between CTHRC1 and the BRAF(V600E) mutation, suggesting its potential utility as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in human colon cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. The original experimental data related to the research results in the article will be provided without reservation if necessary.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rumeng Zhang, Zhihao Wang, Huan Wang, Lin Li, Lin Dong, Lin Ding, Qiushuang Li, Linyan Zhu, Tiantian Zhang, Yong Zhu, Keshuo Ding

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









