Identifying key inflammatory genes in psoriasis via weighted gene co-expression network analysis: Potential targets for therapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bb.2024.10327Keywords:
Psoriasis, hub gene, inflammation-related genes, chemokine, immunohistochemistry, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA)Abstract
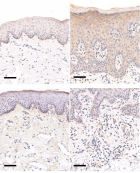
Psoriasis is a globally prevalent chronic inflammatory skin disease. This study aimed to scrutinize the hub genes related to inflammation and potential molecular mechanisms in psoriasis. Utilizing mRNA expression profiles from public datasets GSE13355, GSE78097, and GSE14905, we set up a comprehensive analysis. Initially, we selected differentially expressed genes (DEGs) from psoriasis and control samples in GSE13355, followed by calculating inflammatory indices using genomic set variation analysis (GSVA). Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was then applied to link significant modules with the inflammatory index. This process helped us identify differentially expressed inflammation-related genes (DE-IRGs). A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was established, with the molecular complex detection (MCODE) plug-in pinpointing six chemokine genes (CCR7, CCL2, CCL19, CXCL8, CXCL1, and CXCL2) as central hub genes. These genes demonstrated pronounced immunohistochemical staining in psoriatic tissues compared to normal skin. Notably, the CCR7 gene exhibited the highest potential for m6A modification sites. Furthermore, we constructed transcription factor-microRNA-mRNA networks, identifying 139 microRNAs and 52 transcription factors associated with the hub genes. For the LASSO logistic regression model, the area under the curve (AUC) in the training set was 1, and in the two validation cohorts GSE78097 and GSE14905 were 1 and 0.872, respectively. In conclusion, our study highlights six chemokine genes (CCR7, CCL2, CCL19, CXCL8, CXCL1, and CXCL2) as potential biomarkers in psoriasis, providing insights into the immune and inflammatory responses as pivotal instances in disease pathogenesis. These findings pave the way for exploring new therapeutic targets, particularly focusing on chemokine-associated pathways in psoriasis treatment.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: GSE13355, GSE14905, and GSE78097. Any additional queries should be directed to the corresponding author for further elucidation.
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 huidan Li, Xiaorui Wang, Jing Zhu , Bingzhe Yang, Jiatao Lou

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









