Internodal HER2 heterogeneity of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.3970Keywords:
Breast Cancer, HER2, gene protein assay, GPA, tumoral heterogeneity, lymph nodes, metastasisAbstract
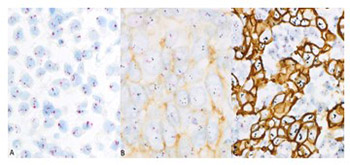
Determination of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status is important for adequate treatment of breast cancer (BC) patients. The novel HER2 gene protein assay (GPA) is particularly convenient, as it allows the simultaneous assessment of HER2 protein expression and gene amplification at individual cell level. Here we investigated the frequency of internodal HER2 heterogeneity in axillary lymph node macrometastases of BC patients and compared HER2 status between primary breast tumor and its metastases. We included a total of 41 female patients operated between 2014 and 2015 for primary BC with axillary lymph node macrometastases. Representative paraffin blocks of metastatic lymph nodes were sectioned and the slides were stained using the GPA in 38 BC cases. GPA results were assessed according to the ASCO/CAP 2013 criteria. We analyzed 12586 individual tumor cells, 120 cells per section of each metastatic lymph node. HER2 status differed between the primary tumor and its metastases in 5/38 cases (13.2%). In patients with at least two metastatic nodes, the HER2 status of lymph node metastases was only slightly different in 4/23 cases (17.4%). Our results indicate rare but substantial differences in HER2 status between primary breast tumor and its axillary lymph node metastases that may direct the choice and outcomes of targeted therapy in BC patients. The impact of the rare and subtle internodal HER2 heterogeneity evidenced in this study remains uncertain. Determining the HER2 status of lymph node metastases in BC seems to be rational, but assessing a limited number of metastatic nodes may be sufficient.
Citations
Downloads
References
World Cancer Research Fund International / American Institute of Cancer Research: Diet, nutrition, physical activity and breast cancer. https://www.wcrf.org/sites/default/files/Breast-cancer-report.pdf
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, Baselga J, Norton L. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:783–792.
Killelea BK, Chagpar AB, Horowitz NR, Lannin DR2. Characteristics and treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer: 43,485 cases from the National Cancer Database treated in 2010 and 2011. Am J Surg. 2017 Feb;213(2):426-432.
Nitta H, Kelly BD, Padilla M, Wick N, Brunhoeber P, Bai I, et al. A gene-protein assay for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2): brightfield tricolor visualization of HER2 protein, the HER2 gene, and chromosome 17 centromere (CEN17) in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissue sections. Diagn Pathol. 2012;7(1):60.
Hanna WM, Rüschoff J, Bilous M, Coudry R a, Dowsett M, Osamura RY, et al. HER2 in situ hybridization in breast cancer: clinical implications of polysomy 17 and genetic heterogeneity. Mod Pathol. 2014;27(1):4–18.
Cottu PH, Asselah J, Lae M, Pierga JY, Diéras V, Mignot L, et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity of HER2/neu expression and its consequences for the management of advanced breast cancer [2]. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(3):596–7.
Song H, Kim TO, Ma SY, Park J-H, Choi J-H, Kim J-H, et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity impacts the response to anti-neu antibody therapy. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(1):647
Seol H, Lee HJ, Choi Y, Lee HE, Kim YJ, Kim JH, et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity of HER2 gene amplification in breast cancer: its clinicopathological significance. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(7):938–48.
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (eds) (2009) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 7th edn. Chichester, John Wiley and Sons
Tot T (2012) The role of large-format histopathology in assessing subgross morphological prognostic parameters: a single institution report of 1000 consecutive breast cancer cases. Int J Breast Cancer 2012:395415
Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ, World Health Organization., et al. WHO classification of tumours of the breast. World Health Organization classification of tumours. 2012. 240 p.
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. TL - 31. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31 VN-r (31):3997–4013.
Zardavas D, Irrthum A, Swanton C, Piccart M. Clinical management of breast cancer heterogeneity. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12 381-394, 2015
Pekar G, Gere M, Tarjan M, Hellberg D, Tot T. Molecular phenotype of the foci in multifocal invasive breast carcinomas: Intertumoral heterogeneity is related to shorter survival and may influence the choice of therapy. Cancer. 2014;120(1):26–34.
Pakdel AF, Memar B, Anvari K, Shandiz FH, Ivari S. Comparison of Estrogen, Progesterone and Her2 Receptors in Primary Breast Cancer and Paired Metastatic Lymph Nodes: An Immunohistochemical Study. 2017;10(5).
Cho EY, Han JJ, Choi Y, Kim K, Oh YL. Comparison of Her-2, EGFR and Cyclin D1 in Primary Breast Cancer and Paired Metastatic Lymph Nodes: An Immunohistochemical and Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization Study. 2008;
Aurilio G, Disalvatore D, Pruneri G, Bagnardi V, Viale G, Curigliano G, Adamoli L, Munzone E, Sciandivasci A, De Vita F, Goldhirsch A, Nolè F. A meta-analysis of oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 discordance between primary breast cancer and metastases. Eur J Cancer 2014; 50(2), 277-289.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2013.10.004
Harigopal, M., Barlow, W. E., Tedeschi, G., Porter, P. L., Yeh, I. T., Haskell, C., Livingston, R., Hortobagyi, G. N., Sledge, G., Shapiro, C., Ingle, J. N., Rimm, D. L., Hayes, D. F. Multiplexed assessment of the Southwest Oncology Group-directed Intergroup Breast Cancer Trial S9313 by AQUA shows that both high and low levels of HER2 are associated with poor outcome. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(4):1639-47.
Pekar G, Kasselaki I, Lukacs AP, Dekany C, Hellberg D, Tot T. Equivocal (HER2 IHC 2+) breast carcinomas: gene-protein assay testing reveals association between genetic heterogeneity, individual cell amplification status and potential treatment benefits. Histopathology. 2018 Aug 16. doi: 10.1111/his.13733. [Epub ahead of print]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-12-11
Published 2019-08-20









