Enhancement of bone consolidation using high-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields (HF-PEMFs): An experimental study on rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.3854Keywords:
fracture healing, electromagnetic fields, titanium 6-aluminum-4-vanadium, osteogenic markers, bone remodelling, bone consolidation, in vivo rat model, high-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields, PEMFsAbstract
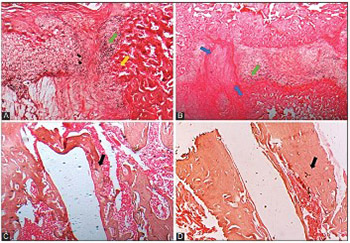
In vitro studies showed that high-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields (HF-PEMFs) increase the activity/expression of early and late osteogenic markers and enhance bone mineralization. The main aim of this study was to investigate the in vivo effects of HF-PEMFs on fracture healing using a rat model. A femur fracture was established by surgery in 20 male Wistar rats. Titanium nails were implanted to reduce and stabilize the fracture. After surgery, 20 rats were equally divided into untreated control and treated group (from the first postoperative day HF-PEMFs at 400 pulses/sec [pps] were applied for 10 minutes/day, for two weeks). Quantitative and qualitative assessment of bone formation was made at two and eight weeks following surgery and included morphological and histological analysis, serological analysis by ELISA, micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), and three-point bending test. At two weeks in HF-PEMF group, soft callus was at a more advanced fibrocartilaginous stage and the bone volume/total tissue volume (BV/TV) ratio in the callus area was significantly higher compared to control group (p = 0.047). Serum concentration of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and osteocalcin (OC) was significantly higher in HF-PEMF group (ALP p = 0.026, OC p = 0.006) as well as the mechanical strength of femurs (p = 0.03). At eight weeks, femurs from HF-PEMF group had a completely formed woven bone with dense trabeculae, active bone marrow, and had a significantly higher BV/TV ratio compared to control (p = 0.01). HF-PEMFs applied from the first postoperative day, 10 minutes/day for two weeks, enhance bone consolidation in rats, especially in the early phase of fracture healing.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2018-10-13
Published 2019-05-20









