Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition improves antioxidative defense during experimental hypercholesterolemia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2014.2264Keywords:
Hypercholesterolemia, COX-2, GPX, SOD, TAS, oxidative stress, inflammationAbstract
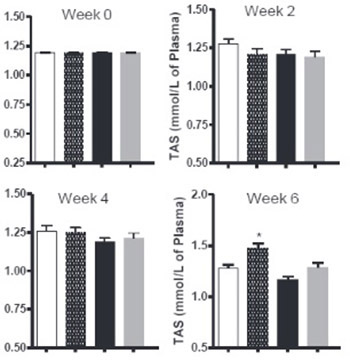
Scientific literature shows that inflammation and oxidative stress contribute in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The oxidative stress is the consequence of an imbalance between the free radical generation and elimination. One source of free oxygen radicals is cyclooxygenase (COX) -2 and, therefore, inhibiting the activity of this enzyme is likely to reduce oxidative stress. In the present study an experimental rabbit model of hypercholesterolemia was developed and the effects of COX-2 inhibitors, nimesulide and celecoxib were observed on the activities of antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and total antioxidant status (TAS). Rabbits were divided into four groups-control, saline, nimesulide and celecoxib, with all groups fed a high cholesterol diet, which only received saline. Low activities of SOD, GPx and TAS were measured in the hypercholesterolemic rabbits pretreated with saline. In the same group, a reciprocal relationship was observed between the LDL-cholesterol concentration and the plasma activities of GPx, SOD and TAS. Rabbits in nimesulide and celecoxib group showed significantly higher activities of SOD, GPx and TAS in hypercholesterolemic rabbits compared to saline group (p<0.05). Our study shows that selective and timely use of COX-2 inhibitors would be useful in preventing the onset and development of atherosclerosis by enhancing antioxidant defence system.
Citations
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
How to Cite
Accepted 2017-07-12
Published 2014-05-20









