Outcomes and prognostic factors for patients with cervical esophageal cancer undergoing definitive radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2019.3873Keywords:
Cervical esophageal carcinoma, radiotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, prognosis, disease management, survival, 3DCRT, IMRT, concurrent chemoradiotherapyAbstract
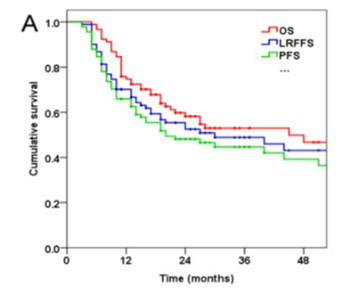
Cervical esophageal cancer (CEC) is uncommon, accounting for less than 5% of all esophageal cancers. The management of CEC is controversial. This study investigated treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of survival in CEC patients undergoing definitive radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT). Ninety-one CEC patients were treated by intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT) between July 2007 and September 2017. The mean prescription dose was 64 Gy (range 54-70 Gy) delivered as 1.8-2.2 Gy per fraction per day, 5 days a week. Out of 91 patients, 34 received concurrent cisplatin-based chemotherapy (CT) including 18 patients who also received neoadjuvant CT. Overall survival (OS), locoregional failure-free survival (LRFFS), and progression-free survival (PFS) were estimated by the Kaplan–Meier method. Prognostic factors of survival were determined in univariate (log-rank test) and multivariate (Cox proportional hazard model) analysis. Treatment-related toxicity was also assessed. Median follow-up time for all patients was 19 months. Two-year OS, LRFFS and PFS of all patients were 58.2%, 52.5% and 48.1%, respectively. Clinical stage was an independent prognostic factor for OS (HR = 2.35, 95% CI: 1.03-5.37, p = 0.042), LRFFS (HR = 3.84, 95% CI: 1.38-10.69, p = 0.011), and PFS (HR = 2.68, 95% CI: 1.11-6.45, p = 0.028). Hoarseness was an independent prognostic factor for OS (HR = 2.10, 95% CI: 1.05-4.19, p = 0.036). CCRT was independently associated with better LRFFS (HR = 0.33, 95% CI: 0.14-0.79, p = 0.012). 3DCRT and IMRT with concurrent CT is well-tolerated and may improve local tumor control in CEC patients. Advanced clinical stage and hoarseness are adverse prognostic factors for OS, LRFFS, and PFS in CEC.
Downloads