BIX01294 suppresses osteoclast differentiation on mouse macrophage-like Raw264.7 cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2013.2339Keywords:
osteoclast differentiation, BIX01294, histone methyltransferase, Raw264.7 cellAbstract
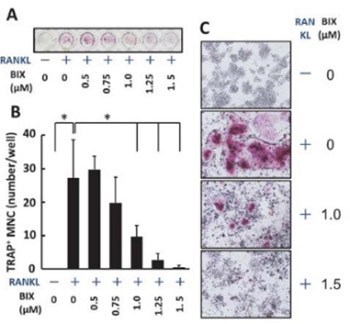
Gene expressionis controlled by epigenetic mechanisms including histone methylation. Osteoclasts are bone-resorptive cells that differentiate from hematopoietic-precursor cells by receptor activator of nuclear factor-KB ligand (RANKL) stimulation. Although BIX01294, a specific inhibitor of G9a, which works as a histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methyltransferase, reportedly changes cellular differentiational stage, its effect on osteoclast differentiation is unclear. In this study, the effects of BIX01294 on osteoclast differentiation were examined. Here, we showed that BIX01294 dose-dependently reduced RANKL-induced tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase positive multinuclear osteoclast-like cell differentiation from murine macrophage-like Raw264.7 cells. During differentiation, growth rates reduced only less than 14% of those of cells stimulated with RANKL alone by BIX01294 treatment. Moreover, western blot analysis showed that BIX01294 reduced RANKL-induced carbonic anhydrase II and cathepsin K production and decreased RANKL-induced nuclear factor of activated T-cell c1, a master regulatory transcription factor, production during osteoclast differentiation. These results suggest that BIX01294 suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. This is the first report about the effect of BIX01294 on osteoclast differentiation.
Downloads