Increased coronary intervention rate among diabetic patients with poor glycaemic control: a cross-sectional study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2014.2286Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus, glycaemic control, coronary artery disease, revascularizationAbstract
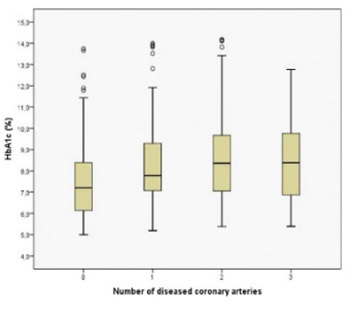
The relationship between glycaemic control and coronary artery disease (CAD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is controversial. In the current cross-sectional study, we addressed the relationship between Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) values and the need for revascularization among diabetic patients undergoing coronary angiography. A total of 301 consecutive patients with known T2DM (age 61.8±10.1 years, 46.2 % women) requiring coronary angiography due to CAD symptoms were included. T2DM patients were categorized into two groups based on their HbA1c values: 93 (30.9%) diabetics with good glycaemic control (HbA1c≤7 %), and 208 (69.1%) diabetics with poor glycaemic control(HbA1c>7 %). A total of 123 patients (40.9%) required revascularization. The revascularization rate was 28.0% among T2DM patients with good glycaemic control and 46.6% among T2DM patients with poor glycaemic control, respectively (p=0.002). In a logistic regression analysis, the need for revascularization was predicted by poor glycaemic control (Odds Ratio [OR] 2.26, 95% Confidence Interval [CI] 1.32-3.82; p=0.003) adjusted for age, gender, Body-Mass-Index and diabetes duration. Moreover, there was a linear relationship between HbA1c values and number of affected coronary arteries (r= 0.169; p=0.003). Our data suggest that there is a close association between poorglycaemic control and increased revascularization rate in T2DM, which should be considered in primary and secondary prevention models.
Downloads